The Software as a Service or SaaS business model involves delivering software applications over the internet as a subscription-based service. In this model, the software is hosted by a third-party provider and made available to customers through a web browser or application interface.
Unlike traditional software delivery models where customers purchase and install software on their local systems, SaaS customers pay for access to the software on a recurring basis, typically monthly or annually. This model allows for greater flexibility in pricing, as customers can scale their usage up or down as needed without making a long-term commitment.
SaaS providers (SaaS companies) are responsible for maintaining the software, including updates and security patches, which reduces the burden on the customer. Additionally, SaaS providers often offer customer support and training to help customers make the most of the software.
Overall, the SaaS business model provides several benefits to both companies and customers, including lower upfront costs, scalability, and ease of maintenance and support.
Benefits of the SaaS Business Model for Providers
The software as a Service (SaaS) business model offers several benefits to providers, including:
- Recurring Revenue: In contrast to traditional software models, where revenue is produced through one-time purchases or upgrades, SaaS providers typically offer subscription-based services, which offers a more predictable and consistent revenue stream. Providers are able to invest in product development, better plan for the future, and make wise business decisions thanks to this predictable revenue stream.
- Scalability: SaaS providers can easily scale their services up or down based on demand, without the need to make significant investments in infrastructure or hardware. This flexibility allows providers to quickly respond to market changes and adapt to customer needs, which can ultimately lead to increased revenue.
- Reduced Costs: The SaaS model eliminates the need for providers to manufacture, distribute, and maintain physical software products. This reduces costs associated with production, shipping, and inventory management, allowing providers to focus on improving their products and services.
- Faster Time-to-Market: With the SaaS model, providers can quickly deploy new features and updates to their software, often without requiring any action from customers. This allows providers to stay ahead of the competition and respond to customer feedback in a timely manner.
- Improved Customer Relationships: SaaS providers have more opportunities to engage with customers and gather feedback, which can lead to improved customer relationships and a better understanding of customer needs. This can result in higher customer retention rates and increased customer lifetime value.
Overall, these benefits of the SaaS business model can help providers build a sustainable and profitable business in today’s competitive software market.
Advantages that customers can get from the Software as a Service (SaaS) business model.
The Software as a Service (SaaS) business model offers several benefits to customers, including:
- Lower costs upfront: SaaS customers don’t have to buy and install software on their own computers, so they don’t have to pay for expensive hardware or licensing fees. Instead, customers pay for access to the software on a regular basis, usually once a month or once a year. This cuts down on upfront costs and makes budgeting easier.
- Scalability: SaaS customers can easily scale their usage up or down based on their needs, without the need to make significant investments in infrastructure or hardware. This flexibility allows customers to respond to changing business requirements quickly and efficiently.
- Reduced Maintenance: SaaS providers are responsible for maintaining the software, including updates and security patches, which reduces the burden on the customer. This frees up time and resources for customers to focus on their core business activities.
- Accessibility: SaaS applications can be used from any device with an internet connection, so customers can work from anywhere and work with team members remotely. This can increase productivity and improve work-life balance for employees.
- Rapid Deployment: SaaS applications can be set up quickly and easily, and most of the time you don’t need IT support or special training to do it. This allows customers to start using the software immediately and avoid lengthy deployment times.
- Support: SaaS providers often offer customer support and training to help customers make the most of the software. This can improve the customer experience and lead to higher satisfaction rates.
Overall, the SaaS business model gives customers a lot of benefits, such as lower up-front costs, scalability, less maintenance, easy access, quick deployment, and support. These benefits can help customers operate more efficiently, save time and money, and stay competitive in today’s fast-paced business environment.
The Stages or Lifecycle of the SaaS Business:
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) is a business model that delivers software applications to customers through the internet. While there is no one-size-fits-all approach, some companies count it in three stages: development, growth, and maturity; others count it in seven or eight stages. Here are the typical five stages that a SaaS business goes through:
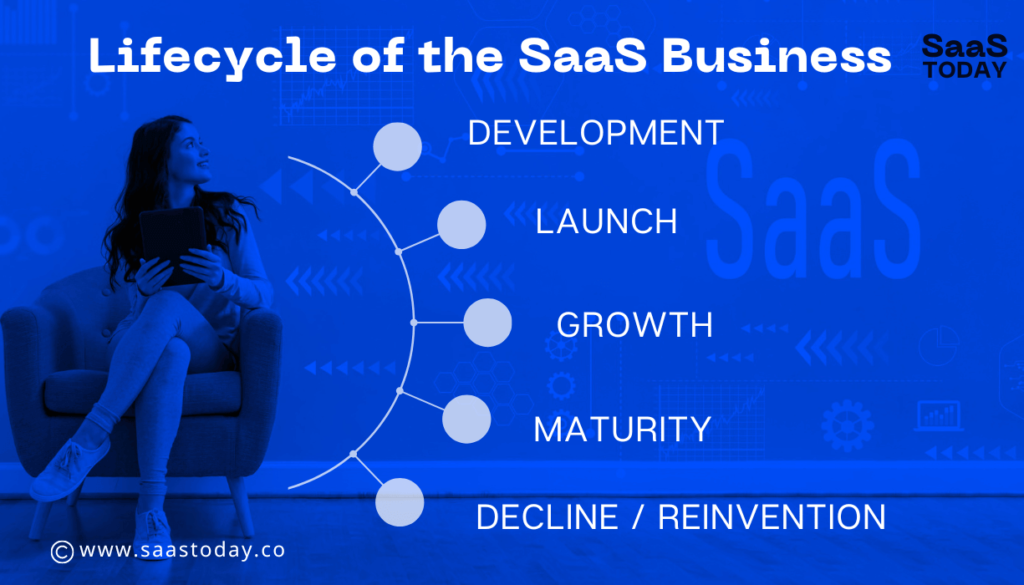
- Development: In this stage, the SaaS product is created. The team decides what features and functionalities the product should have, how it will be developed, and the technology stack it will use. After the product is designed and developed, the team needs to test it to ensure that it meets customer expectations and is ready to launch.
- Launch: After the product is developed, the SaaS business launches it to the public. This is often done in beta testing mode to get feedback from early adopters, and then a full launch is done when the product is ready.
- Growth: Once the product is launched, the SaaS business focuses on growth. This involves building a customer base, increasing sales, and expanding marketing efforts. The company may also work on improving the product and adding new features. The team also needs to consider how the product will be marketed and promoted, as well as how it will be priced, in order to maximize profitability.
- Maturity: As the SaaS business matures, it will have a solid customer base, stable revenue, and a well-established market position. At this stage, the company may focus on optimizing its operations and increasing profitability. This includes further developing existing features, innovating and creating new features, and refining the product to meet new customer needs.
- Decline/Reinvention: A SaaS business may go into a decline phase if it doesn’t keep coming up with new ideas and changing to meet the needs of the market. In this case, the company may need to reinvent itself or its product to stay relevant. To avoid going out of business, the company needs to improve how it runs and make as much money as possible while always coming up with new ideas and adding new features to make sure the product stays relevant to what customers want.
It’s important to note that these stages are not necessarily linear, and a SaaS business may move back and forth between them. Also, the length of each stage can vary a lot based on the product, the market, and the company.
Future of the SaaS Industry
According to the most recent prediction from Gartner, Inc., global end-user spending on public cloud services will increase by 20.4% in 2022 to reach $494.7 billion, up from $410.9 billion in 2021. Spending by end users is projected to reach almost $600 billion in 2023. According to Sid Nag, research vice president at Gartner, “Cloud is the engine that powers today’s digital organizations.” “CIOs are past the era of irrational exuberance in the acquisition of cloud services and are thoughtful in their selection of public cloud providers to drive specific, desired business and technological outcomes in their journey toward digital transformation.” The end-user spending growth rate for infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) is predicted to be 30.6% in 2022, followed by desktop-as-a-service (DaaS) at 26.6% and platform-as-a-service (PaaS) at 26.1%. Because of the new reality of hybrid work, businesses are turning away from traditional client computing solutions like desktops and other tangible in-office tools and toward DaaS, which is expected to drive spending to $2.6 billion in 2022. End-user demand for cloud-native capabilities is what has driven PaaS spending to $109.6 billion.














[…] SaaS refers to a specific type of software-as-a-service (SaaS) offering that is designed to meet the needs of a particular industry or vertical market. Unlike […]
[…] to a recent market report by Technavio, the SaaS market is expected to experience significant growth, with an anticipated increase of USD 147.44 […]
[…] are a great way to recognize and reward excellence in many areas, including SaaS business. Winning an award can boost a company’s reputation, make its brand more known, and bring […]
[…] SaaS market has been growing steadily in recent years, driven by the benefits of cloud-based software […]
[…] as a Service (SaaS) has become a popular business model in recent years, and for good reason. SaaS companies offer a […]